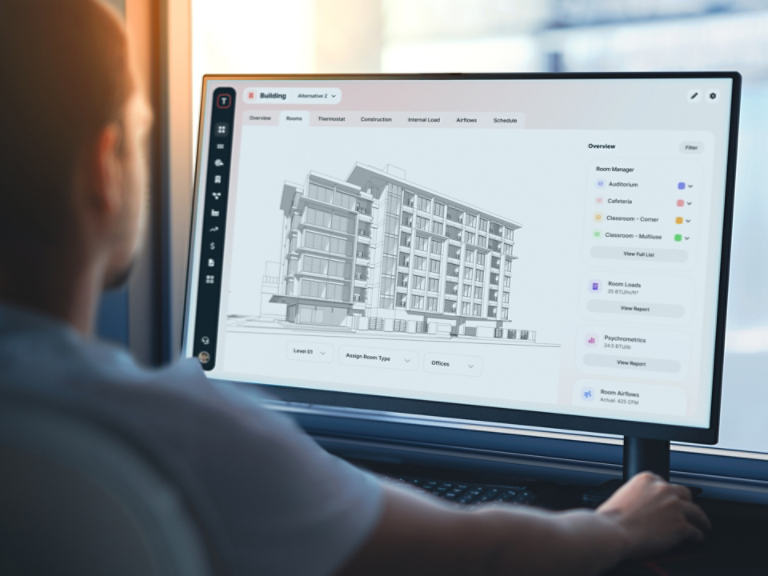
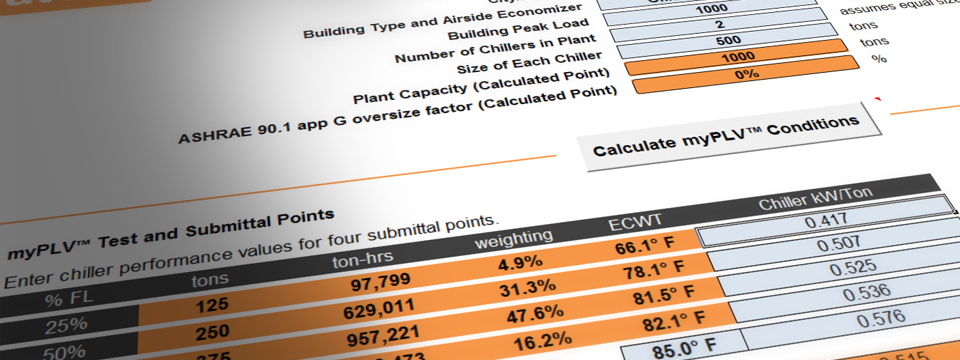
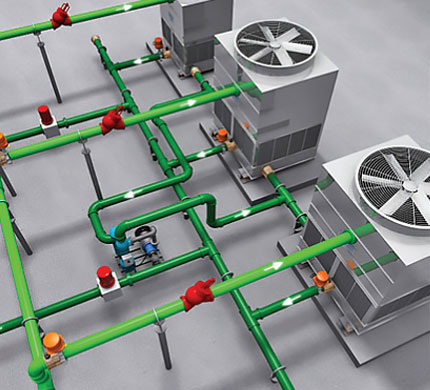
Designing an HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system involves several steps:
- Assess the Building Requirements: Understand the building's purpose, occupancy, and specific needs. This includes considering the type of building (residential, commercial, industrial), the number of occupants, and any special requirements (e.g., server rooms, laboratories).
- Perform Load Calculations: Calculate the heating and cooling loads to determine the capacity required for the HVAC system. This involves considering factors such as building size, insulation, windows, occupancy, and local climate.
- Select Equipment: Choose the appropriate HVAC equipment (e.g., furnaces, air conditioners, heat pumps, boilers) based on the load calculations and building requirements. Make sure the equipment is energy-efficient and meets local codes and standards.
- Design the Ductwork and Distribution System: Plan the layout of ducts, vents, and registers for even distribution of air throughout the building. Consider factors like duct size, material, and insulation.
- Incorporate Ventilation: Account for proper ventilation to maintain indoor air quality. This may involve mechanical ventilation systems, such as exhaust fans and air exchangers.
- Control Systems: Design and integrate control systems (e.g., thermostats, sensors, building management systems) to regulate the HVAC system efficiently.
- Compliance and Standards: Make sure the design complies with local building codes, standards (e.g., ASHRAE®, ANSI), and regulations.
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporate energy-efficient practices and technologies, such as variable speed drives, energy recovery ventilators, and high-efficiency equipment.
- Documentation and Plans: Create detailed plans and documentation, including schematics, specifications, and installation instructions.
- Installation and Testing: Oversee the installation process and conduct thorough testing and commissioning to ensure the system operates as designed.